Download Peripheral arterial Disease e chart: Full illustrated - HC-HealthComm | PDF
Related searches:
Peripheral arterial Disease e chart: Full illustrated
Amazon.com: Peripheral arterial Disease e chart: Full
Peripheral Arterial Disease Detection, Awareness, and Treatment in
The progression rate of peripheral arterial disease in patients with
The Risk of Disease Progression in Peripheral Arterial Disease is
Peripheral Arterial Disease and Its Associated Factors among Type
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) cdc.gov
Clinical presentation of lower extremity arterial disease (LEAD)
Predicting Peripheral Arterial Disease in Men With Erectile
Peripheral Arterial Disease vs. Peripheral Venous Disease NCLEX
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Care Cone Health
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) - CHI Health
Pathophysiology of Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD): A - MDPI
Diagnosis and Treatment of Peripheral Arterial Disease
Confusion of Peripheral Arterial Doppler Waveform Terminology
Peripheral Vascular Disease PVD & Peripheral Arterial Disease
Interpretation of peripheral arterial and venous Doppler
Chapter 20: Peripheral Arterial Disease, Foot Ulcers, Lower
Peripheral Arterial Disease. PAD information Patient
Peripheral arterial disease - SlideShare
QUANTAFLO™ Peripheral Arterial Disease Test
Association between peripheral arterial disease and diabetic
Peripheral Arterial Disease PAD/PVD Symptoms & Treatment
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) - NHS
Arterial Duplex Ultrasonography - Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
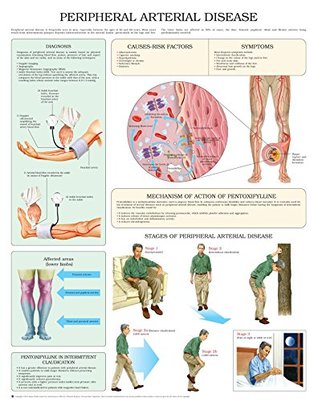
The understanding pad chart presents an overall view of the symptoms and causes of peripheral artery disease (pad). A large graphic shows the vascular system with affected areas. Smaller views accompany the sections on stroke, thrombosis, atherosclerosis, along with blood clotting.
Atherosclerosis affects up to 10% of the western population older than 65 years. It is estimated that 2% of the population aged 40-60 years and 6% of the population older than 70 years are affected with pad (claudication).
Although the absence of a tri-phasic waveform pattern has historically implied peripheral arterial disease,3,15,31,33 this is not consis-tent in the literature, as some authors include bipha-sic as representative of normal flow.
This oversize 22 x 28 (56 x 71 cm) examination-room human anatomy health poster chart defines peripheral artery disease, causes, and risk factors. Did you know that beau's lines (horizontal fingernail ridges) is a possible indication of zinc deficiency, diabetes or pad?.
Peripheral artery disease (also called peripheral arterial disease) is a common circulatory problem in which narrowed arteries reduce blood flow to your limbs. When you develop peripheral artery disease (pad), your legs or arms — usually your legs — don't receive enough blood flow to keep up with demand.
Peripheral arterial disease (pad) occurs when there is significant narrowing of arteries distal to the arch of the aorta, most often due to atherosclerosis. Symptoms vary from calf pain on exercise (intermittent claudication) to rest pain (critical limb ischaemia), skin ulceration and gangrene.
Peripheral arterial disease diagram if you experience pain, achiness or fatigue in your arms, legs or feet when you walk or climb stairs, you may have peripheral.
Tasc working group: management of peripheral arterial disease.
Peripheral artery disease (pad) is caused by a build-up of fatty deposits (plaque) inside the arteries that carry blood from the heart to other parts of the body. When arteries become partly or completely blocked with plaque, the flow of blood is restricted, which interferes with the delivery of oxygen.
Peripheral arterial disease (pad) in the legs or lower extremities is the narrowing or blockage of the vessels that carry blood from the heart to the legs. It is primarily caused by the buildup of fatty plaque in the arteries, which is called atherosclerosis. Pad can happen in any blood vessel, but it is more common in the legs than the arms.
It is accurate at diagnosing pad in people with symptoms up to about 90% of the time.
Peripheral arterial and venous diseases are two types of peripheral vascular disease explanation of the pain (when it happens, characteristics of the pain).
Persistent depressive symptoms and functional decline among patients with peripheral arterial disease. Functional decline in peripheral arterial disease: associations with the ankle brachial index and leg symptoms.
Citation: 2016 aha/acc guideline on the management of patients with lower extremity peripheral artery disease: a report of the american college of cardiology/american heart association task force on clinical practice guidelines.
Peripheral vascular disease (pvd) is a blood circulation disorder that causes the blood vessels outside of your heart and brain to narrow, block, or spasm.
For decades now, doppler technology has been used in order to identify peripheral arterial disease (pad) in symptomatic patients. It’s always been more than enough before, but recent breakthroughs in modern abi technology has led to the manufacturing of th e quantaflo™ peripheral arterial disease test.
Peripheral artery disease vascular disease ekg interpretation np school anatomy and physiology nurse practitioner nurse life medical illustration.
Peripheral artery disease (pad) is an abnormal narrowing of arteries other than those that supply the heart or brain. When narrowing occurs in the heart, it is called coronary artery disease, and in the brain, it is called cerebrovascular disease.
Noninvasive spectral doppler waveform assessment is a principal diagnostic tool used in the diagnosis of arterial and venous disease states. With 200 million people affected by peripheral artery disease worldwide 1,2 and 600,000 hospital admissions yearly for venous thromboembolic disease in the united states, 3,4 establishment and adoption of nomenclature for spectral doppler waveform.
Peripheral artery disease patients living with this condition should be aware of several things. As studies indicate, peripheral artery disease occurs when the plaque builds up in your arteries and there is a decreased blood flow to legs and limbs due to the blockages.
Arterial conditions, such as peripheral artery disease (pad) and critical limb ischemia (cli), and venous conditions, such as deep venous disease (dvd) and superficial venous insufficiency (svi) can produce notable changes in the skin, especially on the legs and feet.
Sep 19, 2001 context peripheral arterial disease (pad) is a manifestation of systemic diabetes was determined from the clinical record (based on a chart diagnosis or use criqui mh, fronek a, barrett-connor e, klauber mr, gabri.
P a d e x e r c i s e t r a i n i n g t o o l k i t� a g u i d e f o r h e a l t h c a r e p r o f e s s i o n a l s healthy steps p a g e 6 for peripheral artery disease chapter 3 pathophysiology and evidenced-based guidelines deconditioning and worsening: obesity, hypertension hyperlipidemia hyperglycemia thrombotic risk.
High levels in the blood increase the risk of heart disease, heart attack, stroke and clogged arteries (atherosclerosis). If your levels are high, your doctor will likely be aggressive to lower your ldl and other risk factors, have you take low-dose aspirin twice a day, and have you follow a mediterranean diet.
Peripheral vascular disease assessment in the lower limb: a review of current and emerging non-invasive diagnostic methods. The role of imaging in peripheral arterial disease, peripheral arterial disease – a practical approach.
Peripheral artery disease (pad) is now the preferred term for partial or complete obstruction of ≥1 peripheral arteries. 1 in this review, pad refers to atherosclerotic occlusive disease of the lower extremities. Other terms used for this condition are peripheral vascular disease, peripheral arterial occlusive disease, and lower extremity.
Peripheral arterial disease is considered to be a set of chronic or acute syndromes, generally derived from the presence of occlusive arterial disease, which cause inadequate blood flow to the limbs. On most occasions, the underlying disease process is arteriosclerotic disease, mainly affecting the vascularization to the lower limbs; we will.
The peripheral artery disease market size is expected to reach $5,715.
Peripheral arterial disease (pad) afflicts up to 20% of older people and is associated with a an electronic literature search was conducted in december 2010 using the medline database.
Peripheral vascular disease (pvd) refers to diseases of the blood vessels (arteries and veins) located outside the heart and brain. While there are many causes of peripheral vascular disease, doctors commonly use the term peripheral vascular disease to refer to peripheral artery disease (peripheral arterial disease, pad), a condition that develops when the arteries that supply oxygen-rich.
This waveform in a peripheral artery is post-stenotic, suggesting a significant stenosis more proximally. Duplex diagnostic criteria for pad can vary between laboratories. Degree of stenosis estimation is based on peak systolic velocity measurements and velocity ratios as illustrated in the table [21]:.
Jun 17, 2019 diagnosis and treatment of peripheral arterial disease.
Peripheral arterial disease (pad), also called peripheral vascular disease (pvd), is a narrowing of the arteries.
Peripheral arterial disease (pad) is a medical condition that involves the narrowing of arteries, leading to a reduction in the blood flow to the limbs, usually the lower extremities. Pad is one of the many circulatory diseases under the umbrella of peripheral vascular disease (pvd).
In some of her previous work with a wound care specialist she knew that wraps were contraindicated with peripheral vascular disease (pvd), so she asked why ace wraps were being used. She was told the wife wanted the legs wrapped, yet there was no order to do this.
What is peripheral artery disease (pad)? peripheral artery disease, or pad, refers to arterial disease that occurs outside of the heart or brain. In pad, the arteries that carry oxygenated blood throughout the body become narrowed or even blocked, usually as a result of atherosclerosis, or plaque.
Pad is also known as peripheral arterial disease or peripheral vascular disease ( which includes both arteries and veins).
Peripheral arterial disease (pad) is a common circulatory problem in which narrowed arteries reduce the blood flow to your extremities.
Categories: arterial and venous (please refer to the chart in appendix 1 for symptom comparison between these two systems). Both types of vascular disease can have an impact on all organ systems and affect function and quality of life. Peripheral artery disease (also known as peripheral arterial occlusive disease).
Background: peripheral arterial disease (pad) can be diagnosed noninvasively by segmental blood pressure measurement and calculating an ankle-brachial index (abi) or toe-brachial index (tbi). The abi is known to be unreliable in patients with vascular stiffness and fails to detect the early phase of arteriosclerotic development.
Peripheral arterial disease (pad) is a common condition where a build-up of fatty deposits in the arteries restricts blood supply to leg muscles.
Peripheral arterial disease is one of the factors linked to diabetic foot ulcers in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, which stresses the importance of early treatment of this vascular disease. Multivariate studies are recommended in order to research its participation in the genesis of the ulcer.
Peripheral artery disease (pad) is a common and often underdiagnosed circulatory disease where blood flow to the legs and feet is restricted by the narrowing of blood vessels due to plaque buildup. Left untreated, pad can lead to amputation and put you or your loved one’s quality of life and long-term health at serious risk.
Intermittent claudication in the lower limbs is the most common clinical presentation.
The following are key points to remember from this review on recent advances in antithrombotic therapy for patients with peripheral artery disease (pad): pad affects over 200 million people globally and is a cause of significant morbidity, mortality, and disability due to limb loss.
The statistical update presents the latest data on a range of major clinical heart and circulatory disease conditions (including stroke, congenital heart disease, rhythm disorders, subclinical atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, heart failure, valvular disease, venous disease, and peripheral artery disease) and the associated outcomes.
Peripheral artery disease narrows arteries in your legs, limiting blood flow. Are you one of the 8 million americans affected by pad? learn more about pad causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment.
Anyone with symptoms or signs of peripheral artery disease (pad) should be tested. Some people should be screened for pad even in the absence of symptoms or signs, such as individuals older than 65 years, or those older than 50 with risk factors like diabetes or smoking.
Peripheral artery disease is a narrowing of the peripheral arteries serving the legs, stomach, arms and head. (“peripheral” in this case means away from the heart, in the outer regions of the body. Both pad and coronary artery disease (cad) are caused by atherosclerosis.
For the management of peripheral arterial ulcers have focused on two primary object-ives: determining if there is adequate blood flow to heal the wound, and assessing for signs and symptoms of peripheral arterial disease (pad).
Pad can be caused by the accumulation of cholesterol, calcium, and plaques on the internal walls of the arteries. This is especially true for the arteries that supply the extremities. With peripheral arterial disease, the arteries become too narrow. This reduces the flow of blood to different parts of the body.
Post Your Comments: